Biotin is considered a B vitamin. It is a key co-factor in 5 enzymes that are part of the metabolic system that controls energy metabolism.
Biotin is involved with DNA replication and gene expression, and is required for cell growth and differentiation. Biotin can be synthesized by bacteria in the human digestive system, which may contribute to biotin status.
Recommended Dietary Allowances for Biotin
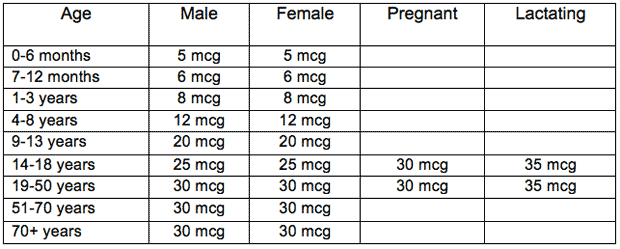 Source: Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine, National Academies
Source: Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine, National Academies
Which Foods Have Biotin?
Chicken liver
Eggs, cooked
Pork
Salmon
Mushrooms
Sunflower seeds
Almonds
Avocado
Strawberries
Sweet potato
Note that the database for biotin in foods in not extensive.
What Happens If You Don’t Get Enough Biotin?
While biotin deficiency due to poor intake is rarely seen, deficiency symptoms can develop after chronic consumption of raw egg white.
A substance in egg white, called avidin, binds biotin in the digestive system and prevents it from being absorbed.
Cooking inactivates the avidin. Again, this problem develops after daily consumption of raw egg white for a long period. Liver disease and an unusual genetic disorder that impairs biotin absorption can also cause deficiency symptoms.
Symptoms of biotin deficiency are unique, and include hair loss, neurologic problems like tingling in the hands and feet, fatigue and a scaly rash on the face and genitals. Because hair loss is one symptom, biotin has been investigated as a treatment for hair loss. However, there’s no evidence that extra biotin is a solution for hair loss that’s not caused by biotin deficiency.


 Are you ready to look better, feel more energized, and get back that youthful feeling you remember having as a kid? I can help you on a journey that will change the way you eat — for good. My
Are you ready to look better, feel more energized, and get back that youthful feeling you remember having as a kid? I can help you on a journey that will change the way you eat — for good. My 














 As a healthy cooking expert, health coach and TV host,
As a healthy cooking expert, health coach and TV host, 



Speak Your Mind