 Vitamin C has many important roles in human health. It acts as an anti-oxidant, protecting cells from damage from free radicals, which are metabolic byproducts.
Vitamin C has many important roles in human health. It acts as an anti-oxidant, protecting cells from damage from free radicals, which are metabolic byproducts.
It’s essential to the production of collagen, a structural protein used in wound healing, tendons, bones, blood vessels and ligaments. Vitamin C is a key part of many other metabolic pathways, from immune function to production of neurotransmitters, metabolism of cholesterol and transport of fat into cells. Vitamin C in the digestive tract enhances iron absorption.
Because vitamin C is involved with so many metabolic systems, especially the immune system, many people advocate very high daily doses as a way to boost immunity and enhance health. So far research does not back up those claims. The current Recommended Daily Intake is quite modest. An adult could get a sufficient dose from a glass of orange juice.
Recommended Dietary Allowances for Vitamin C
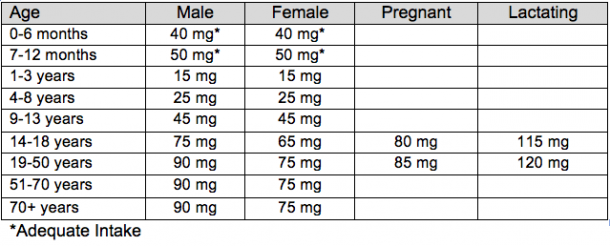 Source: Office of Dietary Supplements, National Institutes of Health
Source: Office of Dietary Supplements, National Institutes of Health
Which Foods Have Vitamin C?
Grapefruit and grapefruit juice
Tangerines
Sweet peppers
Chili peppers
Broccoli
Strawberries
Grape juice (fortified with C)
Brussel sprouts
Papaya
Kiwi
Sugar snap peas
Mango
Pineapple and pineapple juice
Tomatoes
What Happens If You Don’t Get Enough Vitamin C?
The surest sign of severe vitamin C deficiency symptom is scurvy. Hundreds of years ago, sailors on long voyages developed a set of symptoms that were called scurvy: hair loss, easy bleeding, fatigue, joint pain, swollen gums and tooth loss.
These sailors were at sea for months, with little access to high vitamin C fruits or vegetables. Of course, they didn’t know the problem was caused by a nutrient deficiency. But they did figure out the solution, first noted in the 18th Century – eating oranges or lemons.
The variety of scurvy symptoms are related to vitamin C’s role in collagen production, which would be drastically reduced in deficiency, weakening joints, connective tissue and blood vessel walls.
The RDI is intended to prevent deficiency. One goal of current research is to investigate whether the modest recommended intakes should be increased, to promote health rather than just avoid deficiency. Current research is examining the relationship of vitamin C status to a variety of chronic diseases, like heart disease, cancer and the common cold.
Advocates believe the recommended intake for vitamin C isn’t optimal, and higher vitamin C intake could boost immune function and reduce disease risk. At the moment, there is no strong data to support that belief.


 Are you ready to look better, feel more energized, and get back that youthful feeling you remember having as a kid? I can help you on a journey that will change the way you eat — for good. My
Are you ready to look better, feel more energized, and get back that youthful feeling you remember having as a kid? I can help you on a journey that will change the way you eat — for good. My 














 As a healthy cooking expert, health coach and TV host,
As a healthy cooking expert, health coach and TV host, 



Speak Your Mind